AUTOMATED DRIVING
Technology Projects on Automated Driving
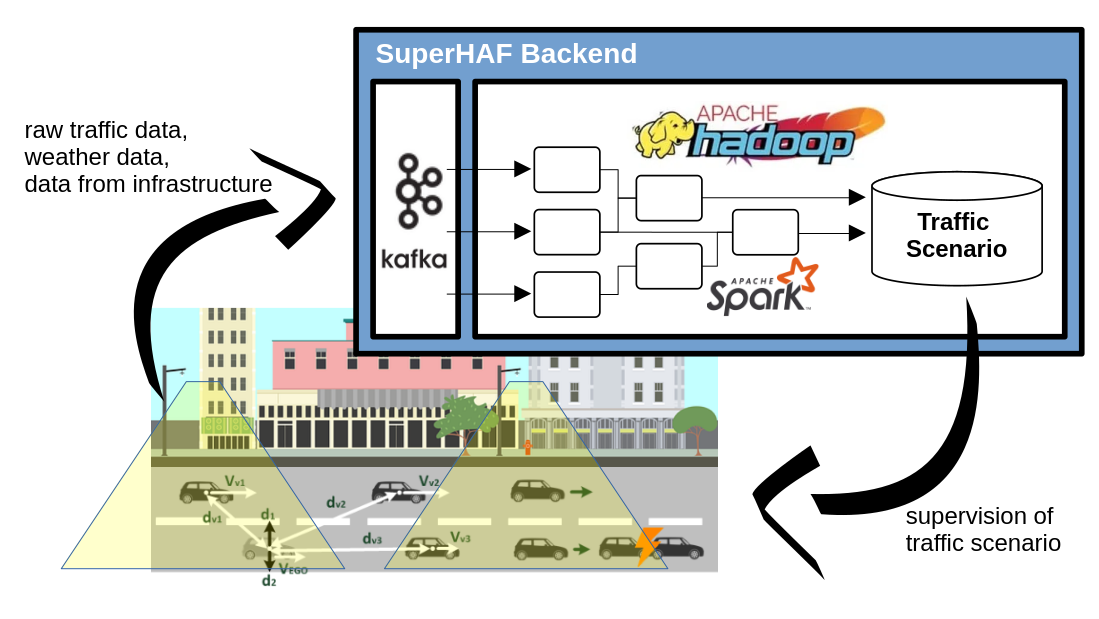
SuperHAF – Supervision of highly automated Driving 2014
When it comes to autonomous driving, most OEMs are pursuing the approach that the vehicles move independently in traffic, in the sense of self-sufficient. This is made possible by sensors built into the vehicle that can see in all directions. The disadvantage is that this sensor technology is very complex and expensive. In addition, sensors only have a limited range and can be disrupted by obstacles.
As part of a technology project, we have developed an alternative, cloud-based approach. Traffic events are recorded and transmitted to the vehicles using low-cost electronics in the form of IoT cameras or IoT radar sensors that are installed in the infrastructure, i.e. in street lamps. This approach is cheaper and also allows to enlarge the limited sensor horizon of the vehicle.
U. Beher, T. Weyrath
Erkennung der Systemgrenzen von hochautomatisierten Fahrerassistenzsystemen mittels infrastrukturgestützter Supervision. In: Automotive meets Electronics (AmE) 2016. Dortmund.
STeelData – Smart Traffic by enhanced and reliable Data
Technologieprojekt, 2016 - 2018
A mobile data service that sends functionally safe data from an IT backend to vehicles in traffic. By qualifying the data as "functionally safe" these data can be immediately used in a safety-relevant driving function, e.g. a function for automated driving.
U. Beher, T. Weyrath
IT-Backend for automated driving and cooperative ADAS. In: ELIV 2017. 18th International Congress. Bonn.
T. Weyrath, U. Beher
Konvergenz von Embedded- und IT-Systemen für das automatisierte Fahren. In: Zeitschrift HANSER Automotive Special 2018.